Further Reading - Visible Light
Total Internal Reflection

Image Source 1: Total Internal Reflection (BBC)
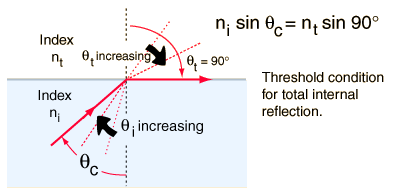
Image Source 2: Total Internal Reflection (hyperphysics)
Total internal reflection is a phenomenon that occurs under certain conditions. It allows for data to travel over distance without loss of data. In terms of endoscopy, light travels from the camera to the detector so that we can see what the camera is 'seeing' within the body.
The first condition is that the light must be travelling toward the boundary between 2 media, of which the medium it is travelling towards has a smaller refractive index than the one it is currently in (for example glass to air). In an endoscope, the tubes that the light travels down have an outer cladding where the refractive index is less than the inner tubing.
The second condition is that the angle of incidence must be greater than the 'critical angle'. The critical angle is the angle at which the angle of refraction travels parallel to the boundary surface. When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the light will fully reflect and refraction will no longer occur. This is total internal reflection. The critical angle can be calculated using Snell's Law given in image 2 where n is the refractive indexes of the media. [V10]
